METALLURGICAL PRODUCTS
Master Alloys
FeSiMg & NiMg

Magnesium treatment is a required step within the production of ductile (DI) iron and compacted (CGI) iron. The primary purpose of introducing magnesium to the molten metal is the formation of spherical graphite, also called "spheroids" or "nodules" (DI) and "compacted graphite" (CGI) respectively. These graphite forms, when produced correctly, are essential to provide the iron with the desired mechanical properties.
- Produced to the highest quality standards
- Critical elements maintained at narrow limits
- Methods for introducing the pre-alloy
| FeSiMg type* | Typical Composition % by weight |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mg |
Ca |
CerMM |
Si |
La |
|
| VL 63 (M) | 6.0 - 6.6** | 1.9 | 0.7 | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 (O) | 6.0 - 6.6** | 1.9 | -- | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 (M) TC | 6.4 - 7.0 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 (M) 3 | 6.0 - 6.6** | 1.9 | 0.3 | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 EGT | 6.0 - 6.6 | 1.9 | 0.15 | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 (M) T | 6.0 - 6.6 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 45 | -- |
| VL 63 LA | 6.2 - 6.8 | 1.8 | -- | 45 | 0.5 |
| VL 73 (M) | 7.0 - 7.6 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 45 | -- |
| VL 73 (O) | 7.0 - 7.6 | 2.5 | -- | 45 | -- |
| VL 7 | 5.7 - 6.3 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 45 | -- |
| VL 53 (M) | 9.0 - 11.0 | 2.0 | 0.7 | 45 | -- |
| VL 53 (O) | 9.0 - 11.0 | 2.0 | -- | 45 | -- |
| VL 53 (S) | 8.0 - 9.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 45 | -- |
| VL 50 (M) | 5.0 - 5.5 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 45 | -- |
| VL 50 (O) | 5.0 - 5.5 | 1.9 | -- | 45 | -- |
| Noduloy 3 | 3.8 - 4.3 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 45 | -- |
| Denodul 5 | 5.0 - 6.0 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 45 | -- |
| NiMg type* | Typical Composition % by weight |
Lumpiness | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mg |
C |
Si |
Fe |
MM |
Ni |
mm |
|
| VL 1 (LC) | 15 - 17.5 | 0.1 max. |
2.0 max. |
1.0 max. |
-- | Remainder | 12-50 150 max. |
| VL 1 (M) | 15 - 17.5 | 2.0 max. |
2.0 max. |
1.0 max. |
1.0 | Remainder | 150 max. |
| VL 4 (M) | 4.5 - 6.0 | 2.5 max. |
2.5 max. |
32-37 | 1.0 | Remainder | Ingots 2.5 kg or 0.8 kg |
| VL 4 (O) | 4.5 - 6.0 | 2.5 max. |
2.5 max. |
32-37 | -- | Remainder | Ingots 2.5 kg or 0.8 kg |
Features:
- Produced with high quality controls
- Tight controls on sizing and chemistry
- Low Mg content makes this suitable for smaller treatment sizes
Features:
- Produced with high quality controls
- Tight controls on sizing and chemistry
Features:
- Produced with high quality controls
- Tight controls on sizing and chemistry
Cored Wire
INFORM M for magnesium treatment
INFORM M Cored Wires are a highly effective and reliable method for introducing magnesium to molten metal. These highly innovative wires are designed in multiple diameters. They are extremely easy to handle and ideal for automation processes. ASK Chemicals INFORM M cored wires are guaranteed to have been produced to the highest quality.
- Well-adjusted compositions to specific foundry needs
- Small addition and exact dosing
- Simple handling, easy to automate
- Good traceability and documentation
- Mg cored wire treatment for DI and CGI
- Offers flexibility with regard to changing initial conditions such as sulfur content, treatment temperature, and iron quality
- Handling and treatment costs can be reduced
- Environmentally friendly because of targeted exhausting
Classification of Mg-treatment wires:
WIRE CONTENT |
DIAMETER |
APPLICATION |
|---|---|---|
| Pure magnesium | • 9 mm • 13 mm |
DI, desulfurization |
| Mixed (Alloys and/or pure elements) |
• 9 mm |
CGI, DI, desulfurization |
| Alloys | • 9 mm • 13 mm • 16 mm |
CGI, DI |
Inoculants
Ladle, in-stream, and cored wire for varying applications
ASK Chemicals Metallurgy offers a wide variety of engineered inoculants for gray (GI), ductile (DI) and compacted graphite (CGI) iron. Each inoculant is unique in design to provide performance characteristics that satisfy today’s demanding casting requirements. These inoculants are produced at our German facility under strict quality control.


- Very good dissolution behavior
- High effectiveness and low consumption
- Uniform graphite precipitation
- Improvement of mechanical properties
- Methods for introducing the inoculants
| Active elements | DI and GI | DI | GI | CGI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Inogen 75 | VP 216/116 (GERMALLOY) |
-- | Inogen 75 | ||
| Ca | -- | -- | ||||
| Ba | SB 5/SB 10 | Inoculoy 63 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Mn | ZM 6 | -- | VP 316 (OPTIGRAN) | -- | ||
| Zr | OPTINOC Z | -- | -- | |||
| Ca | -- | SMW 605 (SMW Formling Typ 1) |
-- | -- | -- | |
| Bi | -- | -- | SAW 304 (SMW Formling Typ 2) |
-- | -- | |
| CerMM | -- | CSF 10 | -- | -- | ||
| Al | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| La | -- | LSF 2 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Sr | SRF 75 | -- | -- | -- | SRF 75 | |
| Ti | -- | -- | -- | LC Graphidox | LC Graphidox | |
Mold Inoculants
GERMALLOY, SMW Inserts and OPTIGRAN
GERMALLOY and SMW Insert are solid cast inserts used for the mold inoculation of ductile iron. They are either placed in the drag portion of the mold or anchored in the pouring basin of very large castings. GERMALLOY is widely used to improve the nodule count of graphite within a casting, as well as enhance its mechanical properties. SMW Insert inoculants, on the other hand, are well known for their ability to eliminate the formation of chunky graphite in heavy section ductile iron. OPTIGRAN is the mold inoculant for gray iron. It provides finer Type “A” graphite in gray iron. Pouring and dissolving time of ASK Chemicals mold inoculants*.
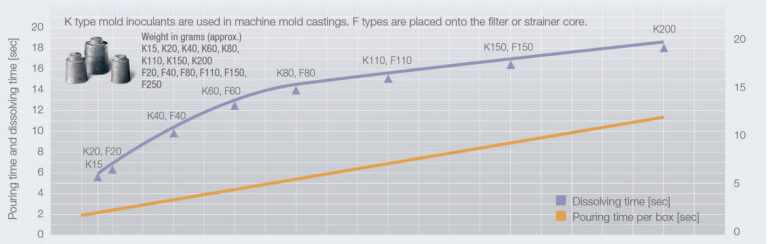

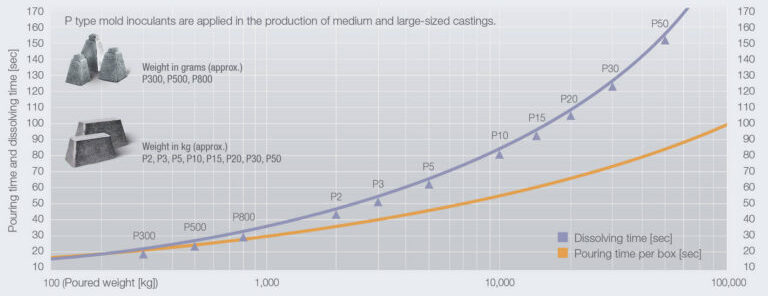

Mold Inoculation Machine Molded - with cast blanks
Pre-Conditioners
Products that ensure a well-prepared base iron
Preconditioning establishes constant conditions in the molten metal. It is important to achieve a proper chemical composition of oxygen and sulfur, especially for the subsequent Mg-treatment processes. It is of upmost importance to achieve process stability, create a uniform base iron and improve the nucleation state of the molten metal. With the pre-conditioning products, ASK Chemicals provides, all of this can be achieved. ASK Chemicals has a wide array of products within this segment to meet your every need.
PRE-CONDITIONER |
IRON |
APPLICATION |
BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Carbide | DI | Furnace/Ladle | Desulfurizes, successfully used for covering FeSiMg during treatment |
| VL (Ce)2 | DI | Ladle | Reduces 02 and S content in the base iron; forms atmospherically stable Ce-0-S compounds; boosts heterogeneous nucleation catalyst |
| DISPERSIT | DI, GI | Ladle | Purification of molten metal; reduction of slag on the ladle and furnace lining; reduction of dross and slag inclusions |
| SilicoMM | Di, CGI | Ladle | Adjusts CerMM content; provides a pre-inoculation effect, i.e. improves nucleation characteristics of iron; produces iron that is more responsive to post-inoculation |
| CerMM | DI, CGI | Ladle | Introducible with alloy or as whole cubes; good at graphite modification; neutralization of interfering elements like lead, antimony, etc. |
Melt Cleaners
Cleaning the melt and minimizing deposits on ladle and furnace linings are essential for ensuring the quality of molded parts and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, it is crucial to avoid slag buildup in ladles, casting, and melting furnaces.
- Reduction of deposits on the ladle and furnace lining
- Reduction of existing slag deposits
- Pre-conditioning of molten metal
- Reduction of dross and slag inclusions
- Pre-conditioning of molten metal
- Reduction of slag on the ladle and furnace lining
- Reduction of dross and slag inclusions
CROWN 8501
NATURAL GRAPHITE PELLET
TYPICAL |
|
|---|---|
| Fixed Carbon | 96% |
| Ash | 4.0% |
| Volatile | 1.4% |
| Ash | 0.02% |
| Ash | 0.30% |
| Ash | 0.008% |
Benefits:
- Fast Dissolution
- Consistent Recovery
- No Dust
- Ultra-low Nitrogen
- Ultra-low Sulfur
- Low carbon footprint
- Ductile Iron
- Gray Iron
- Tap Carbon for steel
- Ladle Carbon for steel
- Cover for Copper
H2251 Titanium
Boron-Aluminum
5% Titanium- 1% Boron-Aluminum Master Alloy
Advantages of using for Grain Refining Aluminum Foundry Alloys:
- Improved feeding
- Reduced chemical segregation
- Increased pressure tightness
- Reduced hot tearing
- Improved mechanical properties
- Improved machinability
- Better response to finishing
- Elimination of salt inclusions
As a general rule, 5% titanium-1% boron-aluminum master alloy is the most potent and reliable additive for general use in grain refining aluminum foundry alloys. Grain refiners should be added to the furnace or ladles close to the end of the processing cycle after the molten metal purification, degassing, and filtration processes. A good starting titanium addition is 0.015 to 0.03%. The amount of grain refiner needed The amount of grain refiner needed to produce optimal castings is often determined empirically.